As described in a paper published June 28 in the journal Nature, a UW ECE research team has invented a new type of LiDAR system that could help self-driving cars “see” distant objects with clarity and precision.
New ‘eyes’ for self-driving cars
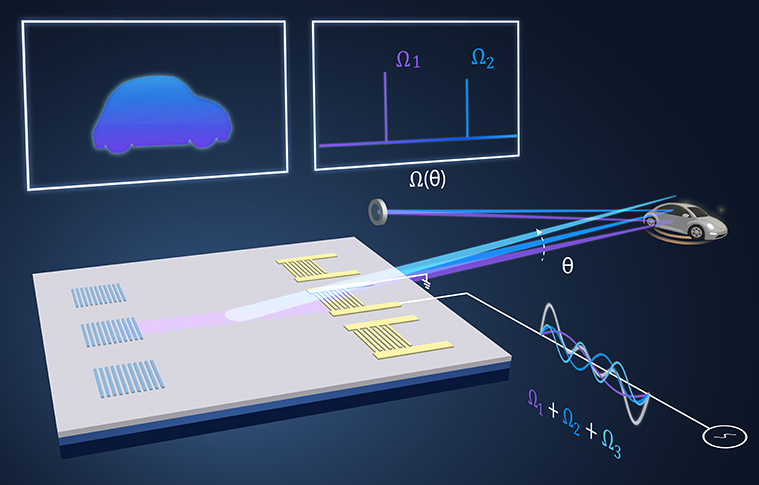

As described in a paper published June 28 in the journal Nature, a UW ECE research team has invented a new type of LiDAR system that could help self-driving cars “see” distant objects with clarity and precision.
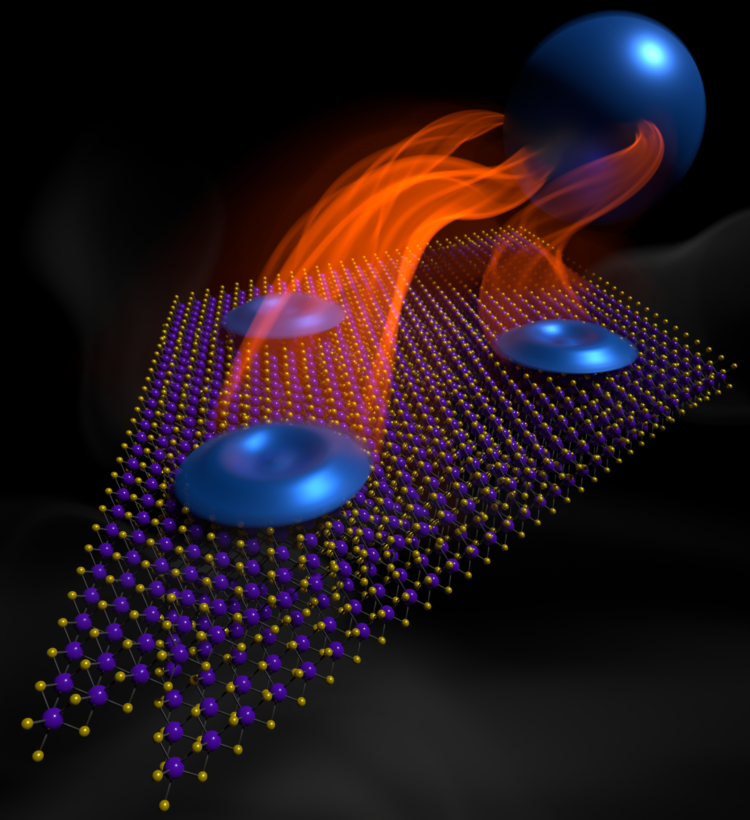
A team of UW scientists and engineers led by Xiaodong Xu has announced a significant advancement in developing fault-tolerant qubits for quantum computing.
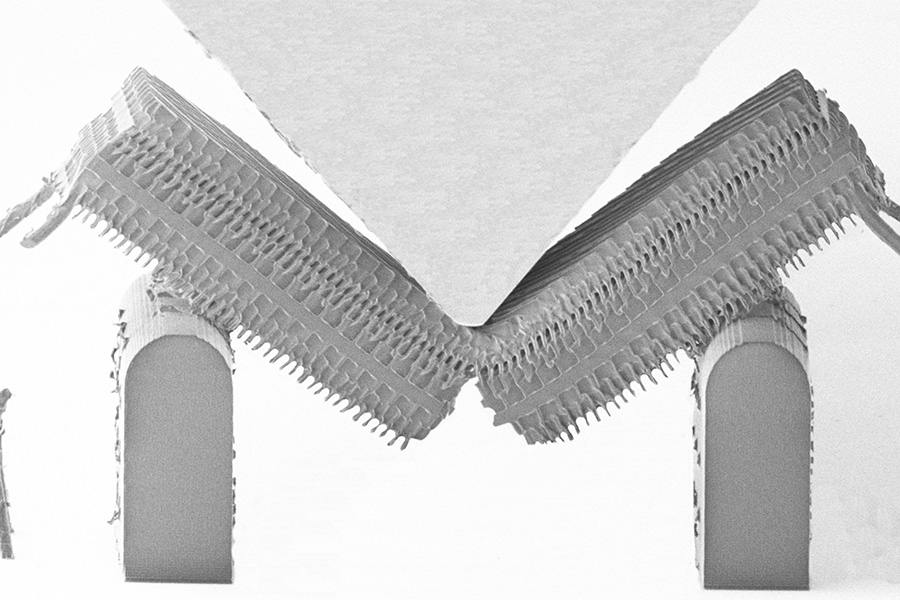
A beetle shell might look like solid armor to us, but it’s actually composed of tiny fibers woven together in complex structures. These nanofibers that comprise many natural materials from shell to skin to cartilage are surprisingly tough and are able to handle force without fracturing.

Every year in honor of National Nanotechnology Day on October 9th, the National Nanotechnology Coordinated Infrastructure (NNCI) hosts a Plenty of Beauty at the Bottom image contest to celebrate the beauty of the micro and nanoscale. Check out this year’s winners and featured images.
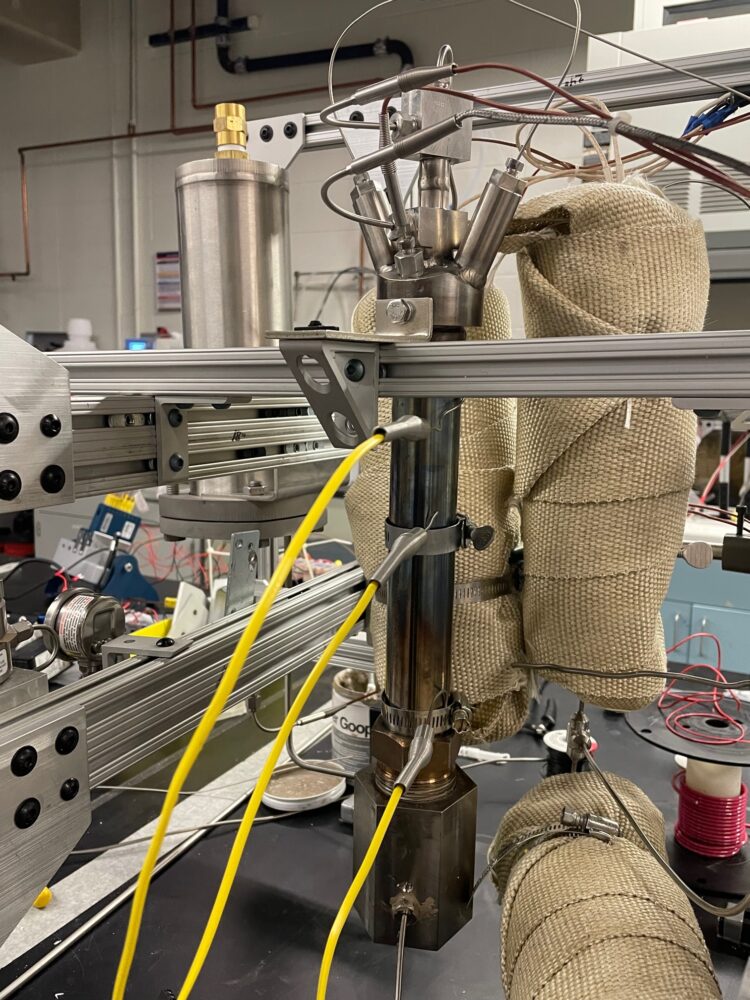

“Forever chemicals,” named for their ability to persist in water and soil, are a class of molecules that are ever-present in our daily lives, including food packaging and household cleaning products. Because these chemicals don’t break down, they end up in our water and food, and they can lead to health effects, such as cancer or decreased fertility. Now a team of researchers at the University of Washington has created a new way to tackle these chemicals — a technology that could help treat industrial waste, destroy concentrated forever chemicals that already exist in the environment and deal with old stocks, such as the forever chemicals in fire-fighting foam.
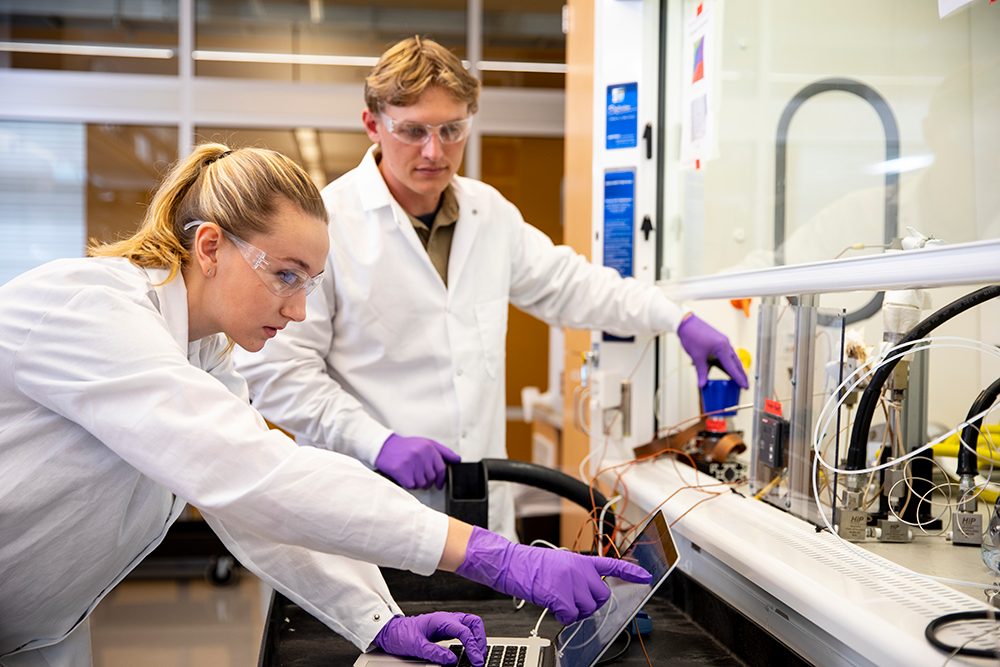

UW researchers have developed a novel method of synthesizing metal-organic frameworks that is fast, cheap, and sustainable.